According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around 466 million people worldwide have disabling hearing loss, and 34 million of these are children. In addition, it’s believed that by the year 2010, nearly 900 million people will experience cognitive decline as a result of profound hearing loss. Hearing loss may result from ear infections, aging, tinnitus, birth complications, genetic predispositions, loud noise, and as a side effect of medication.
If you or a loved one recently received a hearing loss diagnosis and would like to know the treatment options available to you or them, keep scrolling as we explore four common treatment options for hearing loss
1. Hearing Aids
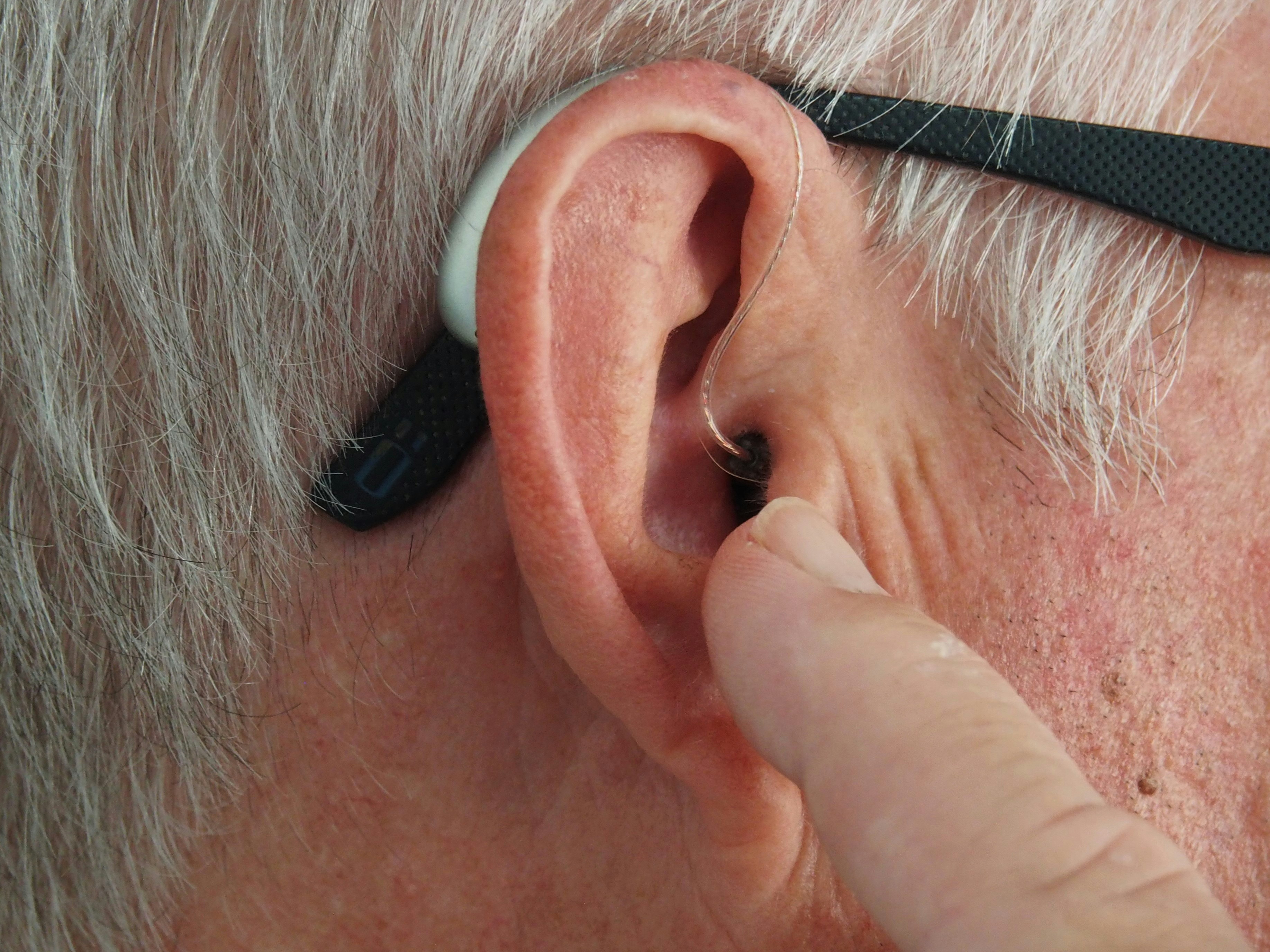
Once diagnosed with hearing loss or a hearing condition that can’t be treated medically, your GP may suggest a hearing test with an audiologist. This hearing test can also detect other hearing problems, like an earwax impaction, for instance.
Hearing aids are available for purchase through a certified audiologist or hearing health professional. After your audiology exam determines the type of hearing loss that you suffer from, you may receive a prescription for a hearing device.
Auditory health is important, so before you book your next hearing test, make sure that your audiologist is board certified. A great way to ensure this is by running a quick search through online directories like the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA), Better Business Bureau, or the consumer protection agency. After your test, you can buy your hearing aid elsewhere, all you have to do is request that your audiologist mail your test results and prescription to you.
2. Medical Treatment

Depending on the severity and type of hearing loss, your doctor may either recommend surgery or medication. A common cause of hearing loss is ear wax impaction. When an earwax build-up blocks the ear canal or the middle ear, your doctor may recommend antibiotics to treat the resulting infection.
However, the COVID-19 pandemic has made it difficult to access over the counter and prescribed medication. Understanding this, organizations like Chepo Meds exist to help people find safe and affordable prescription and non-prescription products online. All you have to do is fill prescription online via their website, or by mail, and wait to have your prescription delivered to you.
3. Assistive Listening Technologies

In some cases, assistive listening technologies may be recommended to work complimentary with hearing aids. As the name suggests, they offer assistance when listening for doorbell rings, phone conversations, watching television, or listening to the alarm — to mention a few.
Assistive hearing devices come in two forms, namely, test display devices, and assistive listening devices. Test display devices work by turning sound into written form. On the other hand, assistive listening devices allow the patient to perceive ambient sound by using a directional microphone — conference microphones, large area listening systems, FM system, amplified telephones, and television listening systems.
4. Cochlear Implant

A cochlear implant is a small electronic device that is used to enhance the symptoms of severe hearing loss. The device is made of two parts, a visible portion that’s fitted in the outer ear, and a second part that is surgically inserted under the skin. It is composed of a microphone, speech processor, receiver, and a group of electrodes. The microphone collects ambient sound, the speech processor organizes this collected sound, and the receiver converts the sound signals to electric signals. The group of electrodes then transmits the sound signals to the auditory nerve.
The cochlear implant works by directly stimulating the auditory nerve, whereas, a hearing aid amplifies ambient sound and directs it into the ear canal. Consequently, while a cochlear implant will not restore normal hearing, it can allow the patient to understand and hear better than they would with a hearing aid.